Flavor bans are challenging e-liquid and hardware manufacturers to produce adaptive products.
By Ellesmere Zhu, 2Firsts
Since China’s e-cigarette control measures took effect on Oct. 1, 2022, consumers can legally purchase only tobacco-flavored vapes in that country. Meanwhile, on the other side of the globe, several U.S. states and cities have banned flavored e-cigarettes. The European Union passed a ban on flavored heated-tobacco products recently, perhaps signaling what may come for flavored e-cigarettes. The once wide range of flavored electronic nicotine-delivery system (ENDS) products is now rapidly narrowing.
Many industry insiders believe the move to ban flavors could expand globally, pushing tobacco flavors into the mainstream market. The current wave of tobacco flavors are testing the tolerances of both e-liquids and the hardware (vaporizers). Manufacturers are now challenged with producing a flavor that customers are willing to purchase and enjoy in markets where any flavor other than tobacco is outlawed.
Reproducing the taste of traditional tobacco in an e-cigarette is no easy matter. It is one of the major hurdles that many enterprises are working on currently. The key to emulating the flavor and taste of traditional tobacco is the vaporizer (coil), a core component of any e-cigarette product. If a vaporizer manufacturer wants to tackle the flavor challenge, it must focus on hardware and software strength.
Technical Troubles
In the face of the global trend of enforcing tobacco-only flavors, e-cigarette manufacturers are having a difficult time making the transition. Most manufacturers rely on diluted tobacco flavors to help customers who have traditionally preferred fruit flavors through the transition, which results in the homogenization of tobacco-flavored vapes. This has many manufacturers trying to determine what features are necessary for a true tobacco flavor. Complicating the issue, no country regulates which combination of flavors make up a tobacco flavor nor how a tobacco flavor should taste.
A representative from Shenzhen Huachengda Precision Industry Co., a global vaping manufacturer specializing in R&D, says that any juice aiming to achieve a global presence must have several characteristics. High recognition, rich fragrance and superior taste are the key to building memorable experiences for customers while dry burning, burnt core, condensation and exploding juice (spitback) are issues to avoid.
The vaporizer, meanwhile, should have a stable structure, which can be achieved by proper assembly and material selection. An unstable liquid absorption rate causes dry burning and burnt cores while unstable heating leads to inconsistency of taste.
Currently, the two most popular vaporizer materials on the market are ceramic wick and cotton wick. The current ceramic wick is hard in texture and easy to assemble, but due to technical limitations, its fine and small-size pore textures result in unstable liquid discharge as the juices with a higher viscosity (such as tobacco flavors) cannot flow through smoothly, according to Chen Ping, CEO and chief engineer for Huachengda.
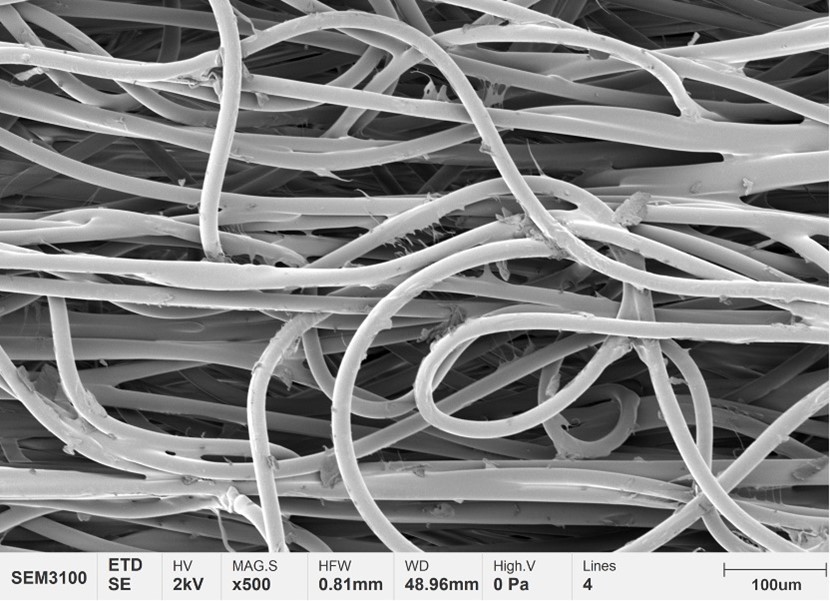

In comparison, the cotton wick is fully permeable and has a larger pore size, which allows the juice to pass smoothly (see Figure 2). However, for all cotton wicks offered on the market today, there is a risk of the wicking being burnt if the temperature on the device is set too high.
“There is a great difference between the characteristics of tobacco-flavored and fruit-flavored e-liquids. If we apply the vaporizer designed for fruit flavor to tobacco flavor, the taste performance and performance of the core is completely different, really an unsatisfactory reproduction of the tobacco flavor,” says Chen. “Taking into consideration the different features between tobacco-flavored and fruit-flavored juice, Huachengda has come up with optimized tobacco flavor through its vaporizers. Ideally, different flavors of juice require different vaporizers, just like one key can only open one lock.”
The Next Generation
After the instability issues are resolved, manufacturers like Huachengda must still find the proper hardware to truly unleash the authentic tobacco flavor in e-liquids. To this end, Chen says his company has invested heavily in R&D. The vaporizer’s structure, materials, formulations and heating element must all be optimized, he explains.
For example, the previous generation of vaporizers were heated by wires, causing overheating, scorching and even burning. However, the heating element comprising a mesh coil can heat the core evenly, thus producing a richer vapor. It has a solid structure that is not easy to burn off, and the flavor can still be maintained at the initial level of quality over long periods of use, according to Chen.
Looking forward on the path of innovation, Huachengda has been developing its new “fiber wick” for which the company applied for a patent in 2021. The manufacturing process of the fiber core is to break the fiber into a pulp and then “stick it together” with a binder to ensure the consistency of the material while improving uniformity, stability and vaporization, according to the company.
However, there is still room for improvement in this technology. When mixed with e-liquid, the fiber wick will absorb the juice and expand gradually. This affects the liquid absorption speed. More performance and material testing are needed before the technology can be applied on a mass scale. As for now, Huachengda has COTTONX, a larger coil that is suitable for disposable e-cigarettes, and its still-in-development fiber wick, a smaller, more compact coil suitable for pod system ENDS products.
“Improving the user experience has always been the focus of the entire industry,” says Chen, adding that a good example is how cotton dividers on the edge of coils were designed to prevent leakage; however, consumers complain of waste because it would absorb some of the liquids. The need to limit wasted e-liquid has spurred further innovation.
The development of the vaporizers differs from that of the microchip, clarifies Chen. “For chips, from 10 nm [nanometers] to 5 nm to 2 nm, the smaller the better,” he says. “But for vaporizers, the development direction is still to be explored. We need to develop and customize the products according to specific laws and regulations and user needs in a decentralized manner. This means that only manufacturers with a large pool of technology reserves and strong R&D can go far in this industry.”

