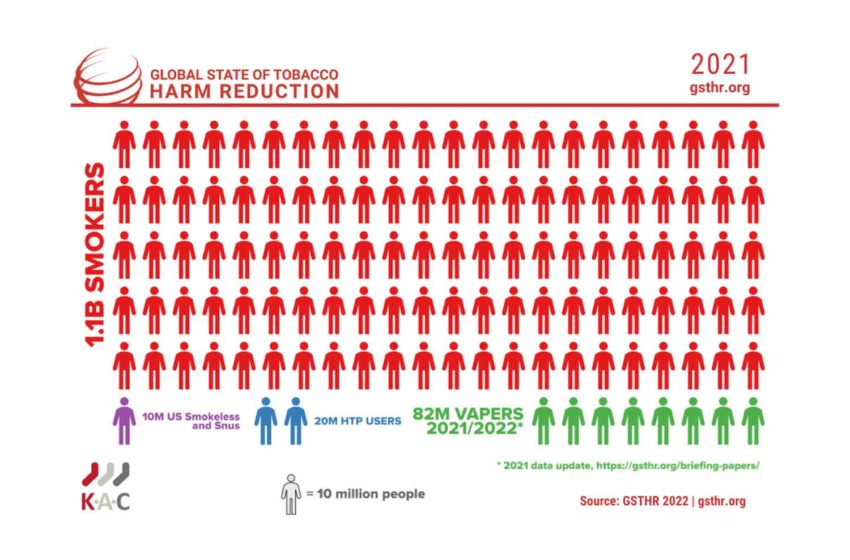
The Global State of Tobacco Harm Reduction (GSTHR), a Knowledge·Action·Change (KAC) project, launches a new series of briefing papers ahead of the publication of its latest report, Fighting The Last War: The WHO and International Tobacco Control on 27 October.
The suite of new GSTHR publications aim to draw attention to, and challenge the direction of travel of, the Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC) Conference of the Parties 9 (COP9), a major global meeting on tackling smoking. The meeting is being held virtually in early November. According to the GSTHR, the FCTC agenda and briefing papers indicate the FCTC Secretariat and leadership are continuing to urge parties against the adoption of tobacco harm reduction approaches that could help save millions of lives.
The GSTHR briefing papers offer analyses, commentaries or explainers on topics related to tobacco harm reduction and its role in combating the death and disease caused by smoking.
The first paper provides a brief overview of both the FCTC and the Conference of the Parties biennial meetings, explaining their role in global tobacco and nicotine policy, as well as highlighting some of the problematic elements of their current operation. A deeper analysis of these issues will be revealed when Fighting The Last War is published later in the month.
The second GSTHR briefing paper focuses on the U.K.’s potential leadership role at COP9. According to the GSTHR, the U.K. has successfully implemented important aspects of a domestic tobacco harm reduction policy, while retaining a strong tobacco control record. Currently, the FCTC project does not reflect the U.K. approach–yet the U.K. is one of the most consistent and generous financial backers of both the FCTC and the WHO. At COP9, the paper argues, the U.K. must be prepared to take a strong line and advocate for policies it has enacted that are demonstrably increasing the numbers of people successfully quitting smoking.
These issues and more will be explored in depth in the GSTHR’s forthcoming report, to be published on Oct. 27 at a hybrid launch event, free to attend online. In Fighting The Last War: The WHO and International Tobacco Control the report’s author, Harry Shapiro, takes a close look at the history, development and often secretive processes of the FCTC COP, its early battles with the tobacco industry – and the range of influences shaping international tobacco control’s response to safer nicotine products in 2021.
The report launch will be broadcast on Oct. 27 from the Kia Oval in London. Two roundtable sessions will be livestreamed from 11 am British Summer Time, with time allowed for questions from those watching in the room and from afar. Will Godfrey of Filter will host the first session, “The FCTC: past, present and future,” which features Harry Shapiro, KAC, report author; Derek Yach, Foundation for a Smoke-Free World, former WHO cabinet director and executive director for noncommunicable diseases and mental health; and Tom Gleeson of the New Nicotine Alliance Ireland.
The second session will be hosted by Jeannie Cameron of JCIC Consulting and will be centered on the “Challenges to making the FCTC an inclusive international framework convention.” Audience members will hear from Ethan Nadelmann, founder, Drug Policy Alliance; Nataliia Toropova, Healthy Initiatives and Professor Gerry Stimson, director, KAC.