A new Yale University study shows that flavor bans cause an increase in underage smoking.
By Maria Verven
A new study by the Yale School of Public Health suggests that San Francisco’s ban on sales of flavored tobacco products may have substantially increased smoking among minors. When San Francisco voters approved a ban on the sale of flavored tobacco products, including menthol cigarettes and flavored e-liquids in 2018, public health groups prematurely celebrated another “win” in their battle to reduce teenage vaping.
Now advocates of the ban must come to terms with the fact that the flavor ban, and most likely similar flavor bans around the world, are inextricably tied to significant increases in teenage smoking rates. According to the study, the odds that high school students would start smoking conventional cigarettes doubled in San Francisco’s school district after the ban was put into effect when compared to districts that didn’t implement a flavor ban, even when adjusting for individual demographics and other tobacco policies.
A Threat to Public Health
Published in JAMA Pediatrics in May 2021, the sole author of the study, Abigail Friedman, associate professor in the Department of Health Policy and Management at the Yale School of Public Health, said the study is the first to assess how complete flavor bans affect youth smoking habits. “These findings suggest a need for caution,” she said. “Even if it is well-intentioned, a law that increases youth smoking poses a threat to public health.”
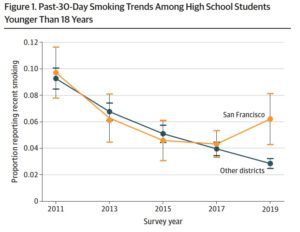
Before the ban was implemented, smoking rates in school districts in and around San Francisco were on the decline. Using data on over 95,000 youth from the Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance System’s 2011–2019 school district surveys, Friedman compared trends in smoking rates in San Francisco versus other districts. The findings revealed a glaringly large discrepancy after the flavor ban went into effect. In 2019, San Francisco’s smoking rates rose to more than twice the average of school districts without a flavor ban. In those districts, smoking rates among youth continued to fall.
E-cigarettes—and particularly those with flavors—have been the most popular tobacco product among U.S. youth since at least 2014. “Some kids who vape choose e-cigarettes over combustible tobacco products because of the flavors,” Friedman said. “For these individuals, banning flavors may remove their primary motivation for choosing vaping over smoking, pushing some of them back toward conventional cigarettes.”
Michael Siegel, professor in the Department of Community Health Sciences at Boston University School of Public Health, said society is at a critical juncture with regard to youth smoking. “It has plummeted to record lows and on top of that, a culture of vaping has completely replaced the culture of smoking,” he said. “The policies enacted in the next year could likely decide what happens next.”
Huge Policy Implications
The results of the Yale study should have huge implications for other states and even other countries when deciding to ban flavored vapes. According to the National Conference of State Legislatures, five states—California, Massachusetts, New Jersey, New York and Rhode Island—have implemented laws banning flavored electronic nicotine-delivery systems (ENDS), and at least 310 localities have passed restrictions on menthol cigarettes and/or flavored tobacco products (including e-liquids), although these laws vary widely.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration implemented a partial ban on the sale of flavored closed-system e-cigarette products in January 2020. The FDA ban exempts menthol and tobacco flavor as well as open tank vaping systems, which tend to be sold in vape shops where age restrictions are more often enforced.
Members of Congress have been pressuring acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock to ban all flavored e-cigarettes, maintaining that flavors are attracting youth to ENDS products. Woodcock has not indicated whether the agency has plans to ban or otherwise limit the sale of flavored vapes, but a decision could be made this fall.
When asked to comment on the trend that youth use of cigarettes was declining while their use of ENDS products was on the rise, former FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb said the trends are not acceptable, even if they are moving in a more positive direction of reduced overall use of tobacco products. “Even if kids are using ENDS [products] instead of cigarettes—and that migration in part accounts for the decline in youth [combustible] cigarette use—that’s still not an acceptable trade,” he said.
Clive Bates, a tobacco harm reduction expert and former director of Action on Smoking and Health U.K., called this argument outrageous, adding that just because a regulatory agency believes young people should not smoke or vape does not mean that is how it plays out in the real world. “Public health is about dealing with the world as you find it—not giving instructions to people who are not listening, uninterested in your views and unimpressed by your authority,” said Bates. “But that doesn’t mean a regulator is absolved of responsibility for the consequences (good or bad) of its actions.”
Since Gottlieb essentially said that the FDA doesn’t care if vaping is helping to reduce smoking, Bates says the FDA is ignoring a big public health benefit that has been a goal of U.S. policy for decades. “The dangerous corollary is [that] the FDA doesn’t care if their anti-vaping measures increase smoking among adolescents. That’s what is so despicable about this lofty attitude—it’s an indifference to the group most at risk,” Bates said. “Yet the FDA doesn’t care if vaping works as an alternative to smoking for adolescents—and this is deeply unethical.”
Generally, regulators do not allow adolescent experimentation to bend adult society and legitimate choices out of shape, especially if these are beneficial to adults, according to Bates. “It should not be taken as a given that adult products that appeal to adolescents should be banned. For many, it is part of being a teenager to sample the forbidden fruits of adulthood,” Bates explains. “We don’t respond to youth experimentation by banning other potentially harmful adult products like alcohol or cannabis just because adolescents use them,” Bates said. “Though it has risen sharply, vaping is not out of the ordinary compared to the prevalence of other risk behaviors. But crucially, it does not actually pose much risk.”
Decisions That Kill
 In June, Health Canada admitted in a regulatory impact statement that its intended flavor ban could lead to an increase in the smoking rate. David Sweanor, an industry expert and chair of the advisory board for the Centre for Health, Law, Policy and Ethics at the University of Ottawa, said that the Health Canada statement is basically saying Canadian regulators know they are going to do something that kills Canadians.
In June, Health Canada admitted in a regulatory impact statement that its intended flavor ban could lead to an increase in the smoking rate. David Sweanor, an industry expert and chair of the advisory board for the Centre for Health, Law, Policy and Ethics at the University of Ottawa, said that the Health Canada statement is basically saying Canadian regulators know they are going to do something that kills Canadians.
“Countries that simply allow alternatives, even without actively facilitating substitution, are seeing dramatic declines in cigarette sales,” Sweanor said, citing Japan, where cigarette sales over the past five years declined at a very rapid pace—far greater than declines in other countries, including the U.S. “I think the biggest constraint on progress is a lack of understanding of the magnitude of substitution effects. To dramatically reduce the use of lethal cigarettes, we need products that are less hazardous and evidence that consumers will switch to them in sufficient numbers to justify substitution as a policy intervention.”
Sweanor said efforts that show the extent of substitution effects are blocked by the absence of funding for such research, obstruction from the anti-vaping moralists and those pursuing a “tobacco-free world” agenda. He also believes that tobacco companies may be reluctant to release sales and consumer research data that would bolster policies designed to undermine their lucrative cigarette business. “Jurisdictions that allow viable alternatives to cigarettes, where such products are as accessible as cigarettes and consumers aren’t given misleading information on relative risks, will see far more rapid declines in smoking,” Sweanor said.
Friedman said the findings from her study strongly suggest that policymakers should be careful not to inadvertently push minors into using the more harmful product. When asked to suggest an alternative policy, she suggested that states consider restricting all tobacco product sales to adult-only (21-plus) retailers. “This would substantively reduce adolescents’ access to tobacco products at convenience stores and gas stations without increasing incentives to choose more lethal combustible products over noncombustible options like e-cigarettes,” she said.
Sweanor added that good policies are contagious and would be replicated. “I am confident that science and rationality combined with consumer advocacy will ultimately win,” he said. “Unfortunately, those opposing such policies can cause lengthy delays, which can result in a tragic and avoidable loss of life.”
Science, Reason and Humanism

Seigel says that there is hope that the Yale study impacts future decisions regarding flavor bans; however, the mainstream anti-tobacco groups are not going to publicize the study because it goes against their preordained conclusions. “If flavor bans are widely adopted, I suspect that many youth who are experimenting with vaping will switch over to cigarette smoking and some will use THC vapes off the black market,” he said. “In contrast, with sensible policies that restrict e-cigarette availability to youth while allowing adult smokers to continue to access them, I think we could drive youth smoking pretty much into the ground—perhaps to a level from which it could never recover.”
Bates questioned how regulators and lawmakers alike could continue with confidence in implementing flavor bans after seeing the results of the Yale study. He added that he seriously questions whether legislators will admit that the ban was a bad idea and reverse course.
“It may put the brakes on some of the worst policy mistakes,” he said. “It’s what many of us have been saying should be expected from a flavor ban. But legislators hate to admit they were wrong, so it will probably lead to calls for tougher enforcement and anti-smoking campaigns rather than realizing that the whole idea is wrong.”
In jurisdictions where viable alternatives to combustible cigarettes are made available, data has shown that the rates of combustible cigarette smoking among youth and young adults is plummeting, according to Sweanor. “More importantly, we are seeing longer term cigarette smokers whose lives are truly on the line, substituting low-risk alternatives,” he said. “People’s response to research depends on motivations. There is a very long and frustrating history of reduced-risk alternatives to cigarettes being attacked by those on a moralist quest to rid the world of nicotine.”
Vaping products are attacked based on accusations about formaldehyde, popcorn lung, e-cigarette or vaping use-associated lung injury (EVALI), cognitive impairments and a seemingly endless list of other supposed hazards, Sweanor explained, adding that these arguments are ultimately shown to be meritless, but vaping opponents never admit to being wrong.
“Such behaviors are hallmarks of conspiracy theorists and those seeking to use the power of the state to impose their moral views on the behavior of others. But where lawmakers are open to science, reason and humanism, studies such as this … [Yale study] are very important,” said Sweanor. “Public health breakthroughs are possible when rational lawmakers get past the panics caused by the moralists. We are staring an historically significant public health breakthrough in the face. The sooner lawmakers recognize this, the sooner we can relegate cigarettes to history’s ashtray.”
The original “Vaping Vamp,” Maria Verven owns Verve Communications, a PR and marketing firm specializing in the vapor industry.






